I hear many people refer to PMI’s PMBOK as a methodology, and methodology it is not. Instead, it is a framework for a set of standards, procedures, and tools that serves as a guideline for project management.
I’ll explain this well-established framework, how to use it to your advantage, and what tools and other methodologies work well alongside it.
I will also detail the most popular PMI certifications primarily based on PMBOK’s guide, which can assist you in becoming a more established (and better-paid) Project Management professional.
Bottom Line Up Front
It’s essential to remember that you show the highest value possible if you want a high salary. By dedicating your time and efforts to qualifying as a PMI professional, you can also show your employer that you’re committed to not only improving your skills but that these skills will become an asset to the organization you work for.
Applying the principles and best practices of PMBOK can help you grow as a project management professional. PMBOK has undergone a more recent change to the 7th Edition, which offers a more flexible and agile approach to delivering projects.
What is PMI’s PMBOK?
Who is PMI?

Before we get into the details, let’s look at what (or who) PMI is.
PMI stands for “Project Management Institute.” PMI was founded in the United States in 1961 and provides professional resources and services to support individuals in developing their careers in project management. It is a non-profit organization run by a board of volunteers.
The service offerings also include networking events and career development opportunities for those in the professional project management sphere.
Read more about PMI here: https://www.pmi.org
What is PMBOK?

PMBOK is an abbreviation for Project Management Body of Knowledge. PMI developed this set of standards, terminology, and best practices and has become a globally recognized gold standard for project management.
PMI has developed several certifications you may or may need to become more familiar with. When I first started in project management, I felt a little lost trying to figure out which certification was indeed “the best” or perceived as the most in-demand Project Management certification.
I have done much research, consulting with those in the recruitment space. As a Senior Project Manager who assists with looking out for top talent, I promise that any PMI certifications are well-respected and sought after. We will look at these in more detail in the next section.
In summary, the Project Management Institute (PMI) is generally considered the top global association that promotes project management by providing professional development opportunities, certifications, and resources for project managers.
PMI’s Certifications and Process
PMI is best known for its project management certifications. Incidentally, this is how I learned about who PMI is and what PMBOK entails. I really enjoy studying but completing qualifications just for the sake of it is not the best use of time.
As such, I’ve spent a great deal of time comparing multiple project management certifications, and PMI remains one of (if not the most) well-respected authorities on project management.
I’ve listed the “top 3” or what I’d deem as the most popular in detail below, but there are additional Agile certifications and micro certifications that PMI offers. You can look at their site for more information: PMI’s Certifications
Let’s dive deeper into the certifications – Who are they for, what they entail, and eligibility for the exam.
PMI’s Project Management Professional (PMP)®

The Project Management Professional (PMP) is one of the most widely recognized as one of the most important and prestigious certifications in project management. It’s held in high regard globally and is most sought after by those in the United States.
You may have noticed that this is one of the only Project Management qualification titles in some people’s email signatures. The course content covers a detailed overview of people, processes, and the business environment within the PMBOK’s project management framework.
Who is it For:
The PMP is best suited for those with a solid understanding of project management and at least three to six years of experience in the field.
What it Entails:
- It has a prerequisite for those registering to study, and you must submit an application to be accepted. The assessment process can take quite some time to complete, and feedback will be provided afterward. You will need to list your detailed project experience, hours, and methodologies used as part of the assessment, and this is why it’s critical to have the experience to be considered by PMI.
- Note – You must complete a set number of PDU (Professional Development Units) every three years to retain your PM status. These can be achieved by completing training or attending networking events and seminars, among other tasks.
- You must pay a renewal fee for the PMP retention process every three years. The cost is payable directly to PMI, and they offer a discount to those members of the PMI.
- The exam format consists of 180 multiple-choice questions, filling in the missing blank, hot area, and matching type of questions. You must complete all questions within the allotted time frame of 230 minutes.
Exam Cost:
An exam fee is required to write the PMP exam (prices are relevant as of May 2023)
- PMI Member: $324.00
- Non-Member: $555.00
Exam/Course Eligibility
You must meet one of the following sets of prerequisites to be eligible:
|
Qualification |
Experience |
| You must hold a four-year completed degree. |
|
OR
| Qualification |
Experience |
| You must hold either a high school diploma OR an associate’s degree. |
|
PROJECT MANAGEMENT TIPS
By completing the Project Management Professional (PMP)®, you will have accumulated the equivalent of four years of project management, which will help your eligibility requirements for the PgMP examination (see below section).
PMI’s Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM)®

Who is it for:
The CAPM is an ideal qualification for those just starting in Project Management and one of the qualifications I generally suggest to my Junior Project Administrators and Coordinators.
What it Entails:
- It offers a basic but broad understanding of key project management fundamentals around the following key sections below.
- Note: the CAPM exam content was recently updated in 2023 to expand beyond the PMBOK® Guide, as previously was the case.
You will need to study the below additional areas of the CAPM course content:
– Agile frameworks/methodologies
– Business analysis frameworks
– Predictive plan-based methodologies
– Project management core concepts and fundamentals - The newer exam format consists of 150 questions which must be completed in the allotted time frame of 3 hours.
- Source: https://www.pmi.org/-/media/pmi/documents/public/pdf/certifications/capm20ecofinal.pdf
Exam Cost:
An exam fee is required to write the CAPM exam (prices are relevant as of May 2023)
- PMI Member: $180
- Non-Member: $240
Exam/Course Eligibility:
| Qualification |
Experience |
| You must hold either a high school diploma (GED – general educational development) or the equivalent level for those outside the United States. | You should have completed at least twenty-three contact hours of project management training or education. |
PROJECT MANAGEMENT TIPS
By completing the Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM)®, you will have accumulated the equivalent of thirty-five hours of project management experience. Completing your CAPM is an excellent step in the right direction to further your career and assist with becoming eligible for the PMP exam (see above)
PMI’s Program Management Professional (PgMP)®

Who is it for:
The PgMP is for senior-level project or program managers with extensive experience managing multiple large-scale projects. The PgMP is not for the faint-hearted; the exam is advanced and possibly one of the most challenging project management certifications to attain.
What it Entails:
- The rigorous examination will assist you in leading successful programs within your organization. In addition, it will aid you in applying the most up-to-date methods and best practices in program management.
- The exam format consists of 170 multiple-choice questions that must be completed within 4 hours.
- Note – as with the PMP, the PgMP requires you to complete a set number of PDU (Professional Development Units) every three years to retain your PM status.
Exam Cost:
An exam fee is required to write the PgMP exam (prices are relevant as of May 2023)
- PMI Member: $640.00
- Non-Member: $800
Exam/Course Eligibility:
To be eligible to complete the PgMP, you must sit a panel review and ensure you meet one of the two sets of prerequisites:
| Qualification |
Experience |
| You must hold either a high school diploma (GED – general educational development) or the equivalent level for those outside the United States. |
|
OR
| Qualification |
Experience |
| A completed four-year degree |
|
Salary Bands and Demand for Individuals with PMI Certifications

As much as I love my job, it’s also important to feel valued, and for some, that translates into how well we’re paid in our current roles.
A big reason I have explored several of these certifications is to have more knowledge when dealing with both internal teams and external clients and have a level of negotiation power regarding potential job opportunities.
Completing any of the PMI certifications will undoubtedly give you an edge against your peers and increase your earning potential considerably.
- As a certified PMP, you could earn a 32% higher salary than those peers who are not PMP holders.
According to Glassdoor (relevant as of May 2023), the differences in salary scales in the United States still show a drastic pay increase opportunity:
- The median salary for a Project Manager with a PMP is around $116,867 per year
- The median salary for a Project Manager WITHOUT a PMP is around $84,969 annually
Source: https://www.glassdoor.com/Salaries/project-manager-pmp-salary-SRCH_KO0,19.htm
Why Do We Follow the PMBOK Guide, and What Are the Benefits and Disadvantages of it?
Please note that the most recent PMBOK® Guide is now the Seventh Edition version. The 6th Edition was officially “retired” on 31 March 2022, and therefore, once all printed copies are sold out, there will be no reprints of this version as it undergoes the phasing out of this Edition.
The details below follow the most recent (7th Edition) version of the PMBOK guide.
Here is an overview of PMI’s latest Edition: https://www.pmi.org/pmbok-guide-standards/foundational/pmbok

As mentioned, PMI’s PMBOK is the gold standard for Project Management and those wanting to become established in their careers. PMBOK is very process-oriented, and the qualifications are not simple to achieve.
As a Project Manager, you’ll need to maintain these yearly. There are significant benefits to this; let’s explore them below.
Benefits of using PMBOK
- As a skilled Project professional in the PMBOK framework, your skills become more in demand, and you can become a sought-after individual in your field.
- I find it becomes easier to manage projects without additional overheads and with a far higher success rate by following the process steps that we’ll look at next.
Disadvantages of PMBOK
- Some teams I’ve worked with do not favor the exceptionally process-orientated nature of PMBOK, and it can be quite a challenge to have all individuals enjoy this approach.
- With rigidity comes a lack of flexibility which even I have found challenging when working with software projects that require far more agility and innovation. The PMBOK guide has recently been adapted to include an “Agile Practice Guide” to cater to this.
Now that we have a good idea of the benefits, let’s look at what they are and how to apply them.
The Twelve New Principles of PMBOK
With the launch of the 7th Edition PMBOK guide and the emergence of flexible and agile project delivery has evolved, the focus has shifted to a set of 12 principles (also known as PMBOK Standards) rather than processes (of which there were 49 previously).
The processes are still valuable, but we value the principles more.
- In summary, PMBOK 7th Edition focuses on “principle-based project delivery” instead of a process-based one.
Interestingly there are also 12 Principles outlined in the Agile Manifesto, which form the foundation of Agile Project Management.
These are slightly different from the 12 Principles that form the basis of PMBOK, which dictates how every project manager must act in accordance with the delivery of the project to ensure its success.
A Brief Look at These 12 New Project Delivery Principles:
- Stewardship: This outlines how a project manager must act in accordance with diligence, integrity, care, and trustworthiness.
- Team: A collaborative project team should be created to thrive and achieve shared project success.
- Effectively engage with stakeholders: If you have worked on projects in the past, you may know all too well how communication can make or break a project. This principle focuses on ensuring the project stakeholders are updated to provide the best outcomes that can be achieved.
- Focus on value: Delivering the requirements set out in the business case ensures that the project is kept on track and meets the business goal.
- Systems Thinking: This principle encourages project managers to employ a holistic view when considering the project environment to understand the complex relationships and interactions affecting project outcomes.
- Leadership: One of the key features in Project Management, and PMBOK is no different. However, leadership is different from management in the way it’s executed. This principle encourages the correct leadership behavior to promote project success.
- Tailoring: I can attest that every day and every project is different. With the ever-changing world in which projects run, a tailored approach must cater to unique projects.
- Quality: Project quality can be more readily achieved by considering the stakeholder requirements and objectives.
- Complexity: Projects will become convoluted, uncertain, and tricky at some point due to dealing with multiple individuals, teams, systems, and processes. How we positively navigate these complexities will ultimately help us achieve project success.
- Risk Responses: Evaluating how we respond to risk is essential for every project. We can mitigate risk by responding proactively ahead of time. It’s vital to also look at how things happened retrospectively to ensure that risks can be avoided in the future and lessons can be learned.
- Adaptability and Resiliency: Similarly to the above, we need to adapt to the inconsistent nature of projects and learn to adapt quickly.
- Change: All projects will be subject to change, and I have yet to work on a project that hasn’t undergone any change, whether due to internal or external requirements or change requests. Managing and communicating this carefully is essential when handling change within various teams and stakeholders.
The 8 Performance Domains of PMBOK
The PMI defines a Project Domain as “a group of related activities that are critical for the effective delivery of project outcomes.”
These Project Domains are created in such a way that they should interact harmoniously throughout your project. Thus prioritizing the guidance of how you interact and facilitate the process to achieve the desired outcomes rather than operating from a set of stringent processes.
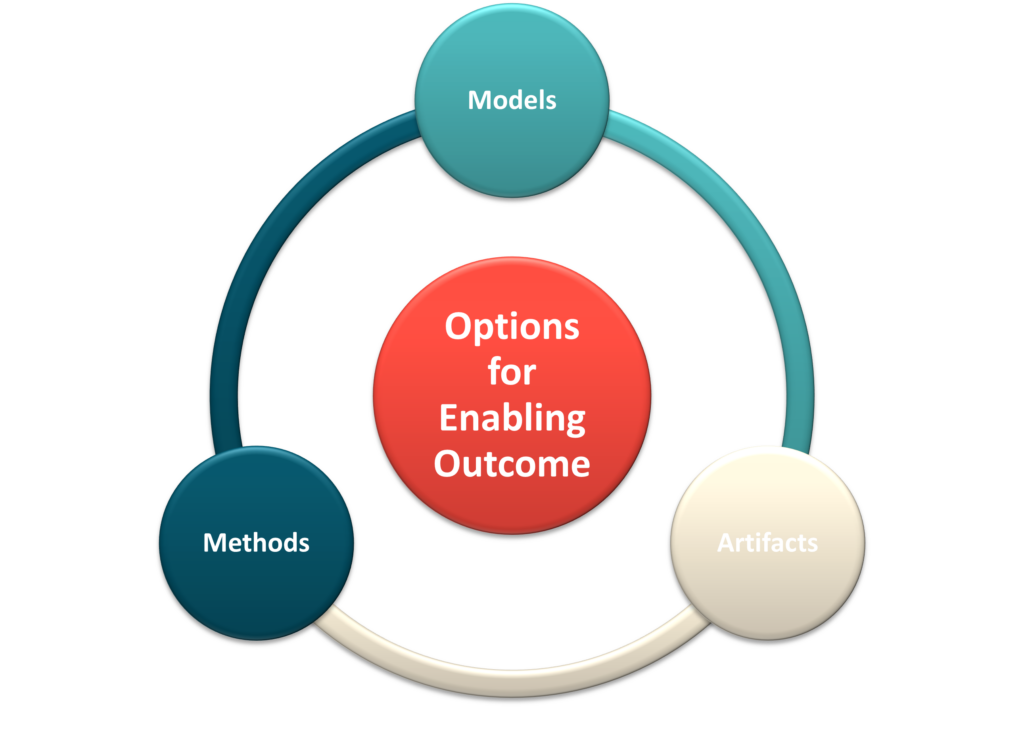
The Models, Methods, and Artifacts of PMBOK
PMBOK 7th Edition guide now incorporates a section that compiles generic models, methods, and artifacts employed by project practitioners.
This section provides a concise overview of each model, method, or artifact and identifies the project performance domains that are most relevant or offer the most significant benefits.
Models, methods, and artifacts must be helpful, valuable, and fit for the project’s purpose.
You can think about these in reference to how they enable the project outcome.
- A MODEL is a cognitive approach to a process, framework, or phenomenon.
- A METHOD represents the approach to accomplish a specific outcome, result, or project output.
- An ARTIFACT refers to templates, documents, outputs, or project deliverables which are generated throughout the project lifecycle.
FAQs about PMI’s PMBOK Project Management
Answer: Yes, although most require some formal project management experience, some excellent entry-level qualifications exist. You could be eligible to complete your CAPM, provided that you have at least twenty-three contact hours of project management training or education and your high school diploma.
Answer: Both versions are applicable, and the 7th Edition is an extension of the 6th Edition. If you are preparing for the PMP exam, you should study the 7th Edition. Remember, the PMP exam is not an examination of the guide, and you should use the online content that PMI offers to help you prepare for the exam (https://www.pmi.org/pmbok-guide-standards/standards-plus). The examination content has been revised to include additional Agile principles and focuses on competency-based questions.
https://www.pmi.org/certifications/project-management-pmp/earn-the-pmp/pmp-exam-preparation/pmp-reference-list
Answer: Until now, the PMBOK guide 6th Edition framework was based on a more traditional approach to project management (also called “Waterfall”). However, as technology has progressed and the need for more flexible and faster turnaround times has emerged, the PMBOK guide has adapted to this.
Conclusion
PMBOK is constantly changing and adapting to the latest technologies and project management, as we’ve seen with the latest 7th Edition. Even if you don’t complete one of the formal exams I mentioned above, I recommend using PMI’s top global online content available to project professionals’ skills.
By following PMBOK’s Guidelines and detailed principles, professionals can enhance their project management skills, strengthen stakeholder and team communication, and increase the likelihood of project success.
Related read
- What is a Project Management RFP?
- Task Management vs Project Management Compared
- Account Manager vs Project Manager Roles Compared

Tarryn Menzies is a seasoned Senior Project Manager, Agile enthusiast, and the insightful voice behind her expert pieces on Projects Pivot. With a career rooted in hybrid Agile environments, including Scrum, Kanban, and MoSCoW methodologies, her passion for project management is palpable in every article she authors. A certified AgilePM via APMG, Tarryn is well-equipped to delve into the intricacies of project management, leading readers through complex concepts with ease and clarity.
In her current role as an IT Operations & Project Manager, Tarryn consistently achieves a balance of technical proficiency and strategic thinking, making her uniquely suited to interpret the often-intertwined worlds of IT and project management. Her extensive skillset includes Waterfall Project Management, PRINCE2, and Service Delivery, among other things, demonstrating her versatility as a management professional.
Known for her clear communication and problem-solving abilities, Tarryn has a knack for managing stakeholders effectively, steering complex projects towards successful completion. With proficiency in Project Management Software, Jira, and XML, she navigates the digital landscape of project management with ease. Moreover, her familiarity with SaaS and Business Analysis empowers her to engage with the evolving needs of modern project management and she shares all her real-world insights here at Projects Pivot!